EMO is an innovative framework for generating expressive portrait videos with audio-driven animation. By inputting a single reference image and vocal audio, EMO is able to create dynamic avatar videos with a range of facial expressions, head poses, and even synchronize them with the audio. With its ability to support different languages, diverse portrait styles, and fast-paced rhythms, EMO opens up new possibilities for lifelike and engaging character animations. It is scary good!
BEYOND HUMAN SUBJECTIVITY AND ERROR: A NOVEL AI GRADING SYSTEM
The purpose of this paper is to introduce a novel automatic short answer grading (ASAG) system based on AI technology and large language models. The paper aims to address the challenges of grading open-ended questions in education by automating the task, reducing workload for educators, and improving grading consistency.
The main takeaways from the paper are as follows:
- The introduced ASAG system, based on a fine-tuned open-source transformer model trained on a large dataset of exam data from various disciplines, demonstrates high accuracy levels in grading unseen questions.
- In comparison to certified human domain experts, the ASAG system shows less deviation from the official historic grades, indicating greater consistency in grading.
- Leveraging AI technology for grading can help reduce human subjectivity, improve consistency, and ultimately increase fairness in the grading process.
- The paper highlights the potential of large language models and AI technology in developing trustworthy and unbiased grading systems for real-world applications in education.
The paper provides encouraging results regarding the effectiveness of AI-based grading systems and emphasizes the significance of leveraging such technology to enhance the educational assessment process.

Exploring the Connection between AI and Surveillance
Artificial intelligence (AI) and surveillance have become intertwined, shaping various aspects of our lives. As educators, we should equip students with a comprehensive understanding of these concepts and their implications. One effective way to approach this topic is through the exploration of novels that discuss the themes of surveillance. To facilitate this process, Surveilit’s website serves as an excellent resource for us teaching English who wish to introduce AI and surveillance through the lens of literature.
Understanding the Connection
AI and surveillance are deeply interconnected. AI-powered technologies have revolutionized surveillance practices, enabling the collection, analysis, and interpretation of vast amounts of data for monitoring and control. From facial recognition systems to predictive algorithms, AI-driven surveillance tools have the potential to significantly impact individuals’ privacy, civil liberties, and social dynamics.
Why teach about AI and surveillance
1. Critical Thinking Skills: Exploring the connection between AI and surveillance encourages students to think critically about the ethical and societal implications of these technologies. It prompts them to consider questions of privacy, power imbalances, and the trade-offs between security and personal freedom.
2. Digital literacy: In the digital age, understanding AI and surveillance is essential for students to navigate the complexities of the modern world. By engaging with these topics, students develop skills to evaluate and critically analyze the information they encounter, enabling them to be informed digital citizens.
3. Empowering students: Teaching about AI and surveillance empowers students to understand and navigate the systems that shape their lives. It encourages them to question and critically examine the role of technology in society, fostering active engagement and agency.
Surveilit: A valuable resource for educators
Surveilit’s website offers a valuable starting point for us wishing to introduce the topic of AI and surveillance through literature. The website provides a database of novels that explore surveillance themes, allowing educators to select works that resonate with their students’ interests.
By integrating discussions of AI and surveillance into the classroom, we can empower students to navigate the complexities of the digital age and develop critical thinking skills.
- Nouri, S. (2020, December 4). How AI Is Making An Impact On The Surveillance World. Forbes1
- Greenhouse, S. (2024, January 7). ‘Constantly monitored’: the pushback against AI surveillance at work. The Guardian2
- Feldstein, S. (2022, June 7). The Global Struggle Over AI Surveillance: Emerging Trends and Democratic Responses. National Endowment for Democracy3
- IFSEC Global. (n.d.). How is AI changing the security sector? 4
- Surveillance & Society. (2023). Vol. 21 No. 3 (2023): AI & Surveillance5
AI and Academia: Student Perspectives and Ethical Implications (studentPOLL/May 2024)
The purpose of this report is to explore the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) and generative AI tools on higher education, specifically focusing on college-bound students. The report aims to understand the students’ knowledge and utilization of generative AI tools, their familiarity with specific tools, and their expectations and concerns regarding the ethical use of AI in academia.
The main takeaways are as follows:
- College-bound students have a high level of self-reported knowledge of generative AI, with the majority being familiar with these tools.
- The most recognized generative AI tool among college-bound students is ChatGPT, followed by GPT-4, DALL-E, and Copy.ai.
- Approximately one-third of college-bound students are using generative AI tools for their schoolwork, while a smaller fraction utilizes them for their college search and application process.
- College-bound students express concerns about the ethical implications of generative AI tools and expect colleges and universities to educate them on the proper use of these tools.
- There are variations in familiarity with generative AI tools based on students’ gender, academic performance, and academic interests.
- Generative AI tools are used by college-bound students for recreational purposes as well as academic purposes, such as writing assignments and studying languages.
This report serves as a call to action for higher education leaders to address the growing presence of generative AI tools and prepare faculty and staff to support an AI-enabled student population. It highlights the need for discussions on ethical considerations and the integration of AI in the college application process.

The Generative AI Toolkit
The Generative AI Toolkit was created by Cecilia Lo and Maria O’Hara at King’s College London to pull together gamified and playful approaches to upskilling staff & students in the Higher Education sector in the UK and is shared under the CC YB SA License which allows you to share and adapt this with attribution. (Source)

2024 Work Trend Index Annual Report (Microsoft & Linkedin)
The purpose of this report is to provide insights into the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on the workplace and to examine the trends and challenges associated with AI adoption.
The main takeaways from the report are as follows:
- Employees want AI at work: The report highlights that a significant number of knowledge workers (75%) are already using AI in their work. They recognize the potential of AI to improve productivity, save time, enhance creativity, and make work more enjoyable. Employees expect companies to adopt AI to stay competitive.
- AI raises the bar and breaks the career ceiling: The use of AI is seen as a way for employees to excel in their careers. It can help them overcome obstacles and break through the career ceiling. However, there is a concern among employees about quantifying the productivity gains of AI, and some are reluctant to admit using it for their most important tasks.
- The rise of the AI power user: The report highlights the emergence of AI power users who bring their own AI tools to work (BYOAI). This trend is observed across different age groups and is more common in small and medium-sized companies. However, BYOAI approach can limit the strategic benefits of AI at scale and raise data privacy and cybersecurity risks.
- Talent shortage and career opportunities: There is a growing concern among leaders about having enough talent to fill roles that require AI skills. Professionals are considering career changes, and there is an opportunity for individuals who are willing to acquire AI skills and expertise. The report emphasizes the need for organizations to invest in reskilling and upskilling their workforce.
The report highlights the increasing prevalence of AI in the workplace, the importance of AI adoption for companies to remain competitive, and the potential career benefits and challenges associated with AI implementation.

Beyond CheatBots: Examining Tensions in Teachers’ and Students’ Perceptions of Cheating and Learning with ChatGPT (May 2024)
The purpose of this paper is to explore the tensions in teachers’ and students’ perceptions of cheating and learning with the use of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, an artificial intelligence language model. The study examines how teachers and students rank and evaluate examples of students using ChatGPT, and it investigates the criteria they use to determine the level of learning and cheating involved.
The main takeaways from the paper are as follows:
- Teachers and students use similar criteria when ranking examples of students using ChatGPT in terms of learning and cheating.
- Teachers and students generally agree on the aspect of learning with ChatGPT but have different conclusions about cheating.
- The disagreements between teachers and students revolve around four main tensions: (a) using ChatGPT as a shortcut versus as a scaffold, (b) using ChatGPT to generate ideas versus language, (c) getting support from ChatGPT versus other sources, and (d) learning from ChatGPT versus learning without it.
- The findings highlight the importance of including student perspectives in establishing norms and responsible use of AI in education.

Future of Writing in the Disciplines and Professions (White Paper)
This paper addresses the challenges faced in writing instruction and propose a solution using generative AI technology.
The main takeaways from the paper are as follows:
- Disconnect between writing research and student performance: The paper highlights the lack of scalable solutions to help college graduates meet the standards of written proficiency despite extensive research on writing instruction.
- Threat to writing “thoughtfully” in the age of AI: The emergence of generative AI poses a challenge to writing that involves critical thinking and thoughtful expression.
- Four principles central to addressing the writing problem: The paper introduces four principles to tackle the writing problem effectively, including reducing the writer’s cognitive load, supporting extended prewriting activity, directing writing activities through genre knowledge, and supporting review/revision processes.
- Introduction of myScribe: The paper presents myScribe as an AI-enhanced online writing environment that incorporates generative and assessment tools. It aims to support writers throughout the writing process, from initial-phase writing to the completion of the final draft.
- Vision for the future of writing: The authors envision a future where AI technology, when properly harnessed, enhances the writing process by freeing up writers’ time for critical thinking skills, planning, and communicating substantive ideas. They emphasize that AI can make writing more fluid, democratic, and inclusive.
- Features of myScribe: The paper highlights specific features of myScribe, such as the Notes-to-Prose tool that translates a writer’s notes into prose, aiding in reducing the cognitive load of sentence crafting. Additionally, myScribe offers AI-based assessment tools for evaluating drafts from various perspectives, including reader expectations, logical flow, content coverage, and sentence clarity.
Perplexity for Educators
Exciting news for educators! Perplexity is proud to announce the launch of a new course specifically designed for teachers, called “AI Search in Education“. This seven-day course aims to empower teachers with fundamental knowledge about artificial intelligence (AI) and its applications in the field of education.
This course is for educators of all levels. No prior AI experience is required. Whether you’re teaching Science or Language Arts, middle schoolers or seniors, this course will share real-life use cases that you can integrate into your day-to-day.
| Here is a preview of what is included: |
| What is AI? Introducing Perplexity, ChatGPT, Gemini, and Copilot |
| Spotlight: Stephen enriches his lesson plans with AI search |
| Spotlight: Kara prepares for her first Advanced Placement class |
| Spotlight: Jamie researches teacher burnout in education |
| Expert Tips & Tricks with Claire |
| Conclusion & The Implications of AI. |
Public Benefit Corporations and AI
Did you know that Inflection AI (PI) and Anthropic (Claude) are Public Benefit Corporations (PBCs)? Have you ever wondered what it means?
Public Benefit Corporations (PBCs) are a type of corporate structure that signals a business considers a “triple bottom line” – people, planet, and profit1. This means they extend benefits to stakeholders like communities and employees, in addition to focusing on profits.
When Claude and PI declare themselves as Public Benefit Corporations, it means they are committing to not just profit maximization, but also to creating a positive impact on society, workers, the community, and the environment12. They must consider how their decisions affect both shareholders and stakeholders.
This structure introduces capital increases and management modifications, creates extra options when making choices about liquidation or selling, and prepares companies to focus on their mission after going public2. It also provides companies with more sale options2.
To sum up, by becoming Public Benefit Corporations, Claude and PI are signaling that they are committed to balancing financial interests with the broader societal and environmental impacts of their operations12. This could potentially set them apart and possibly prime them for inclusion in Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) funds.
What Are Public Benefit Corporations (PBCs)?

Find the Right AI Tool for the Task (Laura Yost/ 3 May 2024)
Microsoft’s MAI-1 LLM
Microsoft is reportedly developing a new large-scale AI language model, codenamed MAI-1123. MAI-1 is expected to have approximately 500 billion parameters13. This places MAI-1 in a similar league as OpenAI’s GPT-4, which is rumored to have over 1 trillion parameters3. Despite its complexity, MAI-1 is too large to run on consumer devices, suggesting that Microsoft will most likely deploy MAI-1 in its data centers1.
The Brain Behind MAI-1
The development of MAI-1 is being led by Mustafa Suleyman, the former Google AI leader who recently served as CEO of the AI startup Inflection before Microsoft acquired the majority of the startup’s staff and intellectual property for $650 million in March3.
The Future of MAI-1
The exact purpose of MAI-1 has not been determined yet13. However, it’s speculated that the LLM could be integrated into services such as Bing and Azure1. Depending on the progress made in the coming weeks, Microsoft may preview MAI-1 as early as its Build developer conference later this month.
The development of MAI-1 suggests a dual approach to AI within Microsoft, focusing on both small locally run language models for mobile devices and larger state-of-the-art models that are powered by the cloud3. It also highlights the company’s willingness to explore AI development independently from OpenAI, whose technology currently powers Microsoft’s most ambitious generative AI features.
Microsoft reportedly developing MAI-1 AI model with 500B parameters
Report: Microsoft’s New MAI-1 Model May Challenge OpenAI’s Leadership
New Microsoft AI model may challenge GPT-4 and Google Gemini
Peeking Under The AI Hood: Activities to Teach How AI Works For Little Learners (Vicky Sedgwick)
Vicky Sedgwick has generously shared these amazing AI resources for little learners – dive in and explore them today for a fascinating journey into the world of artificial intelligence!
- Slides – “Peeking Under The AI Hood: Activities to Teach How AI Works For Little Learners” – Google Slides link
- AI for CA Lessons linked in slides:
- AI Story Creation (Large Language Models)
- AI Image Creation
- Autodraw (not generative AI)
- Adobe Firefly (also in Adobe Express)
- Canva Magic Studio
- Microsoft Copilot
- Trying Out AI Padlet
- Craiyon
- Books to use to teach about AI in elementary
- ReadyAI AI+ME:
- https://www.amazon.com/AI-Me-4-Book-Series/dp/B08J41BW48/
- Version w/all 5 books & extra activities/puzzles: https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B08NYXRTTG
- AI Club book series: https://www.corp.aiclub.world/ai-books-elementary-primary-school-kids
- AI Meets AI (fiction): https://www.amazon.com/Meets-Connection-AiDigiTales-Artificial-Intelligence/dp/B0C87K7HXT
- Tinker Toddlers Series (some AI related and some other topics):
- https://www.amazon.com/dp/B07P97Y8P7
- Aria and the Self-Driving Car (fiction) https://www.amazon.com/Aria-Self-Driving-Car-Tinker-Tales/dp/1950491080/
- Self-Driving Cars for Kids https://www.amazon.com/Self-Driving-Cars-Tinker-Toddlers-Built/dp/1950491099
- Many Intelligences https://matlo.me/many-intelligences (difficult to get in the US)
- ReadyAI AI+ME:
- More resources to teach about how AI works for elementary students
- AI4K12 Resources: https://ai4k12.org/resources/list-of-resources/
- Thinking with KIBO https://kinderlabrobotics.com/thinking-with-kibo-ai-in-early-grades/
(Grades 1-3/could be adapted to other robots with sensors/sensing & computer sensors – does not actually use AI) - Teaching AI in K-2 Padlet: https://padlet.com/visionsbyvicky/AIinK2
- MIT Raise: https://raise.mit.edu/research-projects/
- Hello Ruby Machine Learning and AI (Love Letters to Computers): http://www.helloruby.com/loveletters#episode9
- ISTE Hands-On AI Projects: http://iste.org/ai
- AIforCA: https://csforca.org/ai
- Kode5 AI Lessons https://www.csiselementary.org/s/kode5
Day of AI: https://www.dayofai.org/
NEURO MERMAID AI (Elle Neal)
It is time to present another brilliant and free AI tool!
neuromermaid.ai is a platform developed by Elle Neal that uses Generative AI to research and visualize new ideas. It is designed to assist individuals, particularly those who are neurodivergent, in overcoming information overload and enhancing their learning experience.
The website offers two main features:
- Chat & Visualise: This feature allows users to interact with the AI and visualize the generated ideas.
- Upload & Visualise: Users can upload their own data and visualize it using the AI.
This website is a powerful tool for visual learning. It can help in creating mind maps and flowcharts to break down complex information into visually digestible chunks. This can be particularly beneficial for neurodivergent learners who may process information differently. Teachers can use these visual aids to enhance their teaching practice and make learning more inclusive. What I really like about it is that students can generate mind maps by inserting a key word/key concept/ a YouTube link/ their own text or a website.
Remember, the website is a tool and its effectiveness will depend on how it is used. It is always a good idea to explore the website and see how its features can best serve your specific needs and your stduents. Check it today!
Example 1:
Example 2:

STOP USING AI DETECTORS!!!
AI detectors like ChatGPT and Turnitin are ineffective in catching students using generative AI. A classroom experiment conducted by a teacher showed that 12-year-olds were able to beat these detectors easily. The experiment also revealed that the detectors falsely accused students and targeted non-native English speakers. Educators are seeking innovative solutions to address this problem.
Despite my repeated discussions on this topic through my blog, it is surprising to observe that some teachers still rely on AI detectors, and I find this situation concerning.
💡 The experiment revealed that AI detectors are not effective in identifying students using generative AI, causing frustration among educators.
💡 Retrospective research on handed-in papers is insufficient; conducting real-time experiments with students is crucial to understanding the effectiveness of AI detectors.
💡 Students with limited experience in generative AI were able to bypass the detectors, proving that it doesn’t require much expertise.
💡 The majority of students were able to beat the detectors within 5-10 minutes, showing that they are not a significant challenge.
💡 The current system of accusing students without concrete evidence is flawed and undermines trust in education.
💡 Proposed solutions like Google Documents and Trojan horses are not foolproof and can be easily circumvented by students.
💡 Educators are seeking more innovative ways to address the AI problem in education and use AI for educational benefits.
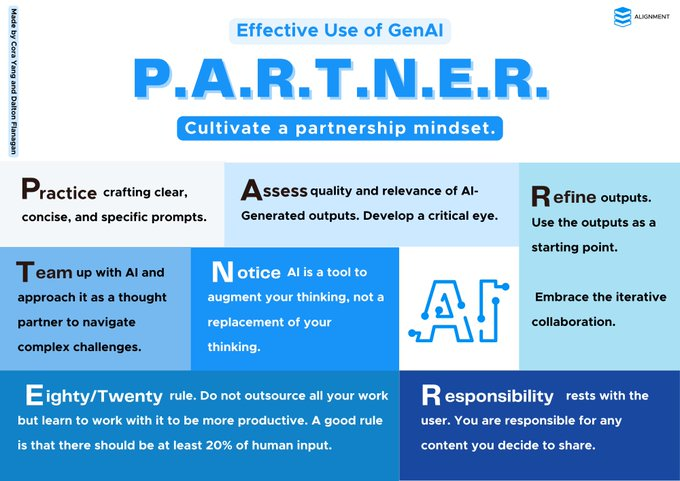
P.A.R.T.N.E.R.- Cultivate a partnership mindset (Cora Yang & Dalton Flanagan)
The “P.A.R.T.N.E.R.” framework by Cora Yang and Dalton Flanagan provides a roadmap for building a productive partnership with Artificial Intelligence.
P: Practice prompt craft
A: Assess outcomes
R: Refine & iterate
T: Team up with AI
N: Note AI is a tool
E: 80/20 rule
R: Responsibility rests with users
Do teachers spot AI? Evaluating the detectability of AI-generated texts among student essays.
This paper presents two experimental studies that investigate the ability of novice and experienced teachers to identify AI-generated texts among student-written essays. The results show that both groups of teachers had difficulty detecting texts generated by ChatGPT, a variant of the GPT-3 model! However, more experienced teachers tended to make more accurate judgments. Additionally, both groups of teachers were overconfident in their judgments.
The study highlights the implications of these findings for grading student essays in educational institutions. It suggests that current AI technologies can generate texts that are indistinguishable from human-written texts, posing a challenge for teachers in assessing students’ writing. The paper provides empirical evidence relevant to the ongoing debate on examination strategies in light of technological advancements.
Trends 2024 (Higher Learning Commission)
This document provides a list of trends in higher education for the year 2024. It is intended to inform and guide institutions in identifying the trends that most impact their institutions and to help them adapt and lead in the changing landscape of higher education. The document covers various topics, including artificial intelligence, paradigm shifts, outcomes and accountability, finances, new business models, short-term credentials, politicization of higher education, civility and safety, mental health, talent management, leadership, and the influence of the triad.
The main takeaways from this document are:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is growing in higher education, with applications for teaching, learning, personalized instruction, and administrative tasks. Institutions need to establish policies on ethical use, ownership, privacy, fraud, and integrity of information.
- Paradigm shifts in teaching, learning, and enrollment are occurring, with online learning expanding, the exploration of three-year bachelor degrees, challenges to shared governance and tenure, and the impact of race-conscious admissions policies.
- Outcomes and accountability are increasingly measured using data analytics, and there is a demand for reliable job placement numbers and evidence-based outcomes. Financial stability, international student enrollments, and risk management are also important considerations.
- Financial challenges and opportunities exist across all sectors of higher education, including small college mergers and closures, deferred maintenance, demographic changes, and the cost of technology.
- New business models are emerging, such as subscription-based course selection and partnerships with employers to design educational programs aligned with workforce needs. Institutions are also restructuring to integrate credit and non-credit offerings.
- There is exponential growth in short-term credentials and new providers, driven by skills-based hiring and the need for comprehensive records. Quality assurance guidelines play a crucial role in navigating the credential marketplace.
- Higher education is increasingly politicized, with elected officials influencing regulations and diversity, equity, and inclusion programs. Presidential election campaigns may include higher education proposals.
Using Artificial Intelligence Tools in K–12 Classrooms (RAND Corporation/Research Report/April 2024)
This research report aims to understand the current state of K-12 teachers’ use of artificial intelligence (AI) tools and the support they receive from their districts in using these tools. The report also explores teachers’ and district leaders’ perspectives on the potential impact of AI on teaching and learning.
Key Takeaways
- AI use among teachers is still uncommon. Only 18% of teachers reported using AI tools in their teaching, with another 15% having tried them at least once.
- Middle and high school teachers and those who taught English language arts or social studies were more likely to be AI users.
- The most common ways that teachers used AI tools were to adapt instructional content to fit the level of their students and to generate materials.
- By the end of the 2023-2024 school year, 60% of districts plan to have trained teachers about AI use.
- Urban districts were the least likely to deliver such training.
- District leaders described focusing more on increasing teachers’ AI use and less on crafting student use policy, primarily because they saw the potential for AI to make teachers’ jobs easier.
Additional Insights
- Teachers who use AI tools are most likely to use them for adapting instruction and generating materials.
- Teachers identified concerns about the role of AI in society, data privacy, and potential bias as the top barriers to expanding their use of AI tools.
- Districts are increasingly providing training to teachers about AI use, but there are disparities in access to this training based on district characteristics.
These findings suggest that AI is beginning to play a role in K-12 classrooms, but its use is still in its early stages. There is a need for more research on the effectiveness of AI tools for teaching and learning, as well as on the best ways to support teachers in using these tools effectively. Additionally, it is important to address the concerns that teachers have about AI, such as data privacy and potential bias.
Claude for iOS is here
Did you know that Anthropic has made an exciting announcement? They have launched the Claude iOS app, bringing the incredible power of Claude to your iPhone! With this new app, you can now access Claude’s features and capabilities conveniently from your mobile device, allowing you to harness its potential wherever you go.
Claude iOS app
With the launch of the Claude iOS app, you can access Claude from anywhere, any time.
The Claude iOS app features:
- Seamless syncing with web chats: Pick up where you left off on a new device.
- Vision capabilities: Use photos from your library, take new photos, or upload files to get real time image analysis.
- Open access: Users on any plan can download the Claude app free of charge.
Whether you’re brainstorming ideas on the go, need a quick answer on a pressing question, or want to analyze scenes and images from the real world, our new iOS app puts the power of frontier intelligence in your back pocket.
To download the iOS app, find us on the Apple App Store.
Exploring the effects of AI literacy in teacher learning: an empirical study
This article explores the effects of AI literacy on teacher learning and investigate the determinants of teachers’ intentions to learn AI. The study aims to promote AI learning among K-12 teachers and contribute to the field of AI education.
The key takeaways from the article are as follows:
- Many teachers lack knowledge of how AI functions and are unable to fully use AI in education.
- Teachers’ perceptions of the use of AI for social good and self-efficacy in learning AI directly influence their behavioral intentions to learn AI.
- Awareness of AI ethics and AI literacy indirectly impact teachers’ behavioral intentions to learn AI.
- AI literacy has a direct impact on teachers’ perceptions of the use of AI for social good, self-efficacy in learning AI, and awareness of AI ethics.
- The study highlights the importance of enhancing teachers’ AI literacy and ethical awareness in promoting effective AI-based teaching.
- The Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) and Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) can be integrated with AI literacy and awareness of AI ethics to predict teachers’ behavioral intentions to learn AI.
These findings provide insights into promoting AI education among K-12 teachers and serve as a foundation for further research and the design of professional teacher programs focused on AI.
Beyond Algorithms: The Irreplaceable Value of Human Connection in Teaching
In today’s world, education must go beyond the digital boundaries marked by the rise of artificial intelligence, and we should never forget the value of genuine teaching occurring in the classroom. As an educator who has dedicated years to the pursuit of shaping young minds, I have witnessed firsthand the power of human interaction in nurturing growth and spurring innovation among my students.
Teaching is not a transfer of knowledge but a complex, intimate dance between educator and student-a journey filled with unexpected twists, enlightening discussions, and rewarding breakthroughs. While AI tools have the potential to revolutionize certain aspects of education, they lack the spark unique to the human touch.
Engaging the whole student
Education is an art that engages students beyond the intellectual level. It prods curiosity, stirs emotions, and ignites a passion for lifelong learning. The vibrant energy shared when exploring new ideas together in a classroom, or the lightbulb moments during one-on-one discussions or debates, cannot be replicated by even the most sophisticated machine learning models.
Let me share with you a moment from my teaching experience: during a field trip to a local grocery store (you can read about it here), one of my students, Hege, was asked to investigate plant-based meat alternatives available at the Rema 1000 store. Driven by the desire to understand consumer preferences, Hege sought out the employees of the store to gain insight into their personal opinions on these products. Even though she could quickly generate an AI report without asking a single person, she wanted to talk to and learn from individuals who stocked and sold these items daily. It was this human connection and the ability to directly engage with the experiences and perspectives of the store workers that inspired her to delve deeper into understanding the human factors influencing the popularity of plant-based items.
Nurturing relationships beyond the screen
In the often-messy labyrinth of adolescence, students grapple with far more than academic challenges; they face real-world problems, navigate social intricacies, and struggle to find their unique voices. As educators, we talk to them face-to-face, not screen-to-screen. We guide their understanding, empathize with their struggles, and mentor them through life’s trials.
I recall when Tor approached me with a heavy heart, torn by a conflict with a close friend. No algorithm can navigate the intricacies of human emotions or provide the empathy and wise counsel necessary to repair a friendship. It is in these human moments that the true essence of teaching shines brightly, illuminating the path for our students as they grow into well-rounded individuals.
Empathy: the AI outlier
The teacher-student relationship is the backbone of effective learning- a connective tissue built on mutual respect and understanding. AI, for all its benefits, cannot comprehend the subtleties of a student’s furrowed brow during a challenging topic or the subtle swing of confidence when they grasp a complex concept. Technology cannot replace a safe space when our students are vulnerable or a nudge towards their potential. These are human experiences that machines cannot replicate.
Consider the moment when Sara, brimming with innovative ideas but struggling with shyness, needed just a bit of encouragement. It was the human connection, our shared laughs, and gentle reassurances that helped her present an award-winning Genius Hour project. AI might have offered critique and useful pieces of advice but could never replicate the warmth of human encouragement.
Complementary, not supplementary
To be clear, I am not discounting the merits of AI in education. Its capabilities in providing personalized learning experiences, automating administrative tasks, and offering instant feedback are truly invaluable. If you have been following my blog for the past 13 months, I hope you have noticed amazing examples of my use of AI/AI tools in my classroom. However, these tools are facilitators, not replacements. They should serve to enhance the educational experience, not diminish the role of human educators.
Our responsibility as teachers extends far beyond the mere use of cutting-edge tools. We shape futures, instill values, and inspire dreams- it is a role that technology cannot, and should not, aspire to replace.
The essential role of the human educator
In conclusion, AI holds significant potential to enhance education, but it should only serve as a tool to support the art of teaching. As we stride forward into a future where AI becomes increasingly pervasive, we must remember that the heart of education beats not through data points and algorithms but through the deep, irreplaceable connections between teachers and students.
—
For every educator embracing the tide of technological advancement, I stand with you, yet urge you to sail carefully, for it is our humanity that will ultimately guide our students to their destinations, not the cold currents of code.

The Possibilities of AI- Sam Altman (OpenAI/Entire Talk/YouTube)
Sam Altman, co-founder and CEO of OpenAI, discusses the possibilities of AI and its impact on society and the future. He emphasizes the need for responsible deployment of AI and the importance of adapting to the changing technological landscape.
Key takeaways:
- Sam emphasizes the need for responsible deployment of AI, recognizing the potential dangers and the importance of adapting to the changing technological landscape.
- He believes that now is the best time to start a company, particularly in the field of AI, as the world is rapidly changing and the opportunities for impact are immense.
- Sam encourages aspiring entrepreneurs to trust themselves and come up with their own ideas, rather than following the consensus, as this is where the most value and impact can be found.
- He acknowledges the need for resilience and adaptability in the face of technological advancements, which will be increasingly important in the future.
- Sam predicts that fusion or solar plus storage will dominate electrical generation in the future, aiming for affordable and abundant renewable energy sources.
- He highlights the importance of a shared mission and teamwork at OpenAI, driving the company’s culture and success in pushing AI research forward.
- Sam recognizes the potential of AI to greatly impact society, but also acknowledges the need for careful consideration of its deployment to ensure positive outcomes and mitigate potential risks.
The rUv Enterprise AI Pocket Guide (Strategic AI Integration/Reuven Cohen, Brenda Cohen, and OpenAI)
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of strategic AI integration, offering insights, methodologies, and best practices to help organizations successfully incorporate AI technologies into their operations and derive maximum value from them.
The target audience includes business leaders, executives, managers, and decision-makers who are involved in strategic planning, technology implementation, and digital transformation initiatives. It is also relevant for AI consultants, data scientists, and professionals working in the field of artificial intelligence.
The guide covers various topics related to strategic AI integration, including the following main takeaways:
- The rUv Method: The document introduces the rUv method, which stands for Responsive, Unifying, and Visionary. This method emphasizes the importance of a lean team approach and highlights key focus areas and requirements for successful AI integration.
- Human-Centric AI: The guide emphasizes the significance of human-centric AI, which focuses on enhancing the enterprise experience by considering the impact of AI on the workforce, collaboration, communication, and future-oriented evolution.
- Micro-Transformation in Enterprise Environments: It explores the concept of micro-transformation, which involves making incremental changes and cultural shifts within an organization to facilitate AI integration. The guide discusses the benefits, challenges, and solutions associated with micro-transformation.
- AI Readiness Assessment and Framework: It provides an assessment framework for evaluating an organization’s readiness for AI integration. The guide outlines the goals of the assessment, the development of the assessment framework, and the process of conducting an assessment workshop.
- Technology and Architecture: The document delves into the technical aspects of AI integration, discussing core architectural elements of an enterprise AI platform, data handling, resource allocation, security and privacy protocols, and interoperability with external systems.
- Prompt Engineering and Large Language Models (LLMs): It explores the use of prompt engineering and LLMs in enterprise AI projects, including considerations for training large language models, crafting effective prompts, and incorporating external data. It also discusses the Prompt Engine System and its benefits.
- Intelligent Agents and Co-Pilot Systems: The guide covers the concepts of intelligent agents and co-pilot systems, their role in enhancing business operations, their development, training programs, and future trends in the field.
- Security and Compliance: It addresses the importance of security and compliance in AI integration, including topics such as zero trust cybersecurity, secure architecture design, data fabric security, incident response, and legal considerations.
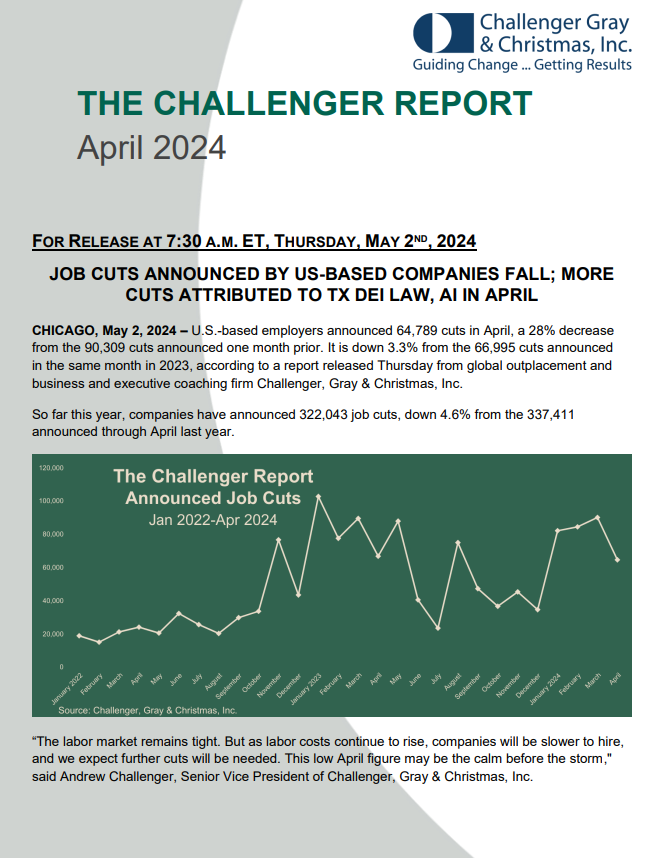
THE CHALLENGER REPORT (April 2024)
This report provides an overview of job cut announcements made by U.S.-based companies in April 2024. The report aims to analyze the trends and factors contributing to job cuts across different industries.
Key takeaways from the report include:
💼Job Cut Trends: In April 2024, U.S.-based employers announced 64,789 job cuts, which is a 28% decrease from the previous month and a 3.3% decrease compared to April 2023.
🚗Industries with the Most Job Cuts: The automotive sector had the highest number of job cuts in April, primarily due to Tesla announcing a reduction of 14,000 jobs. The education industry and health care/products industry also experienced significant job cuts.
🤖Impact of AI: Artificial Intelligence (AI) was cited as a reason for 800 job cuts in April, the highest total since tracking began in May 2023. Companies either shifted their focus to developing AI or implemented it to replace certain tasks and roles.
📜 Texas DEI Law: Texas Senate Bill 17 (SB-17) resulted in 80 job cuts in April. The bill prohibits public higher education institutions in Texas from engaging in diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives.
🤝Hiring Plans: The hiring plans announced in April were the lowest for that month since 2013. U.S. employers announced plans to hire 9,802 workers, and the total hiring plans for the year were lower compared to previous years.
📊Overall Job Cut Trends: Job cuts in various industries, such as technology and media, showed fluctuations compared to the same period in 2023.
FYI: As an English teacher, you could use this report to provide insights into the current job market and factors impacting employment, organizing class discussions or debates on topics such as the causes and consequences of job cuts, the role of technology in the labor market, the significance of diversity and inclusion initiatives in the workplace, and how artificial intelligence will influence workplaces of the future.
The Difference Between Great AI and Great Teaching with Dan Meyer (YouTube)
Dan Meyer emphasizes the importance of holding onto the profound truths about teaching and learning in times of tech disruption. He argues that AI, especially chatbots, fail to invite and develop student thinking, leaving teachers with too much to do. The hype around AI in education has not been met with actual usage, as many teachers find it impersonal and ineffective. Teachers and students are asking for more important things like safety, community, autonomy, and respect, which tech and business leaders seem unwilling to provide. I highly encourage educators to watch Dan Meyer’s talk!
🧠 Theoretical high-level ideas about teaching and learning are crucial in times of tech disruption. They provide the grounding and orientation needed to navigate the changing educational landscape effectively.
🚫 AI, especially chatbots, fails to invite and develop student thinking, leaving teachers with the burden of retracing their own developmental path and ineffective learning for students.
📚 Teachers play a crucial role in gathering and understanding the pedabytes of context that students bring to their education. This context cannot be captured by chatbots and is essential for effective teaching and learning.
🏫 Teachers and students have more important needs, such as safety, community, autonomy, and respect. These fundamental aspects of education are often overlooked in the hype around AI and technology in the classroom.
🤝 Tech and business leaders must prioritize the needs of teachers and students over pushing AI and technology as a solution. Building relationships, providing support, and addressing the real needs of educators and learners should be the focus.
📚 The gap between the hype and actual usage of AI in education suggests that teachers are smart and discerning. They see the limitations and lack of personalization in current AI tools and are not easily swayed by marketing or professional development efforts.
💡 The future of AI in education remains uncertain. While there is potential for technology to enhance teaching and learning, it should be seen as a servant of higher ideals rather than replacing or overshadowing the knowledge, principles, and values that educators hold.
Generally Faster-The Economic Impact of Generative AI (April 2024/Andrew McAfee)
The purpose of this report is to explore the potential of generative AI as a general-purpose technology and its impact on economies and societies. The report aims to provide insights into the transformative effects of generative AI, its implications for economic growth, skills and jobs, business transformation, and potential risks and harms.
The key takeaways from the report are:
- Generative AI is a general-purpose technology: Generative AI is identified as a technology with the potential to accelerate overall economic growth and bring about positive transformations in economies and societies.
- Rapid improvement and pervasiveness of generative AI: Generative AI has shown remarkable improvement in its ability to generate relevant and accurate content in response to user prompts. It has the potential to be widely used across various sectors and transform them.
- Economic growth and productivity gains: Generative AI has the capacity to deliver significant productivity gains, leading to faster economic growth. Complementary innovations that leverage generative AI’s capabilities can further enhance its impact.
- Changing demand for skills and jobs: Generative AI will have an impact on the labor market by reducing demand for certain skills, increasing demand for others, and creating demand for entirely new skills and occupations. While concerns about technological unemployment are deemed exaggerated, reskilling programs will be crucial to facilitate workforce transition.
- Business transformation: Generative AI is expected to bring about transformative changes in businesses, enabling improved performance, innovation, and creative expression. It has the potential to enhance the performance of entry-level employees and contribute to addressing wage inequality.
- Novel risks and harms: The report acknowledges that new technologies, including generative AI, pose challenges alongside benefits. It emphasizes the need for understanding and addressing potential risks and harms associated with the widespread adoption of generative AI.
The Global 50 Report (2024/Dubai Future Foundation)
“The Global 50′ report, in its third edition, seeks to explore and capitalise on future opportunities to refine work methodologies and lifestyles, offering insights and best practices to governments, businesses, and civil society worldwide. The report also identifies significant challenges that may impede global advancement, preparing us to face them effectively. Additionally, the report outlines the ten megatrends shaping current and future transformations and their impact on worldwide development.” (Source/p.3)
Litmaps: Your Secret Weapon for Mastering Literature Reviews
As students, we all know the struggle of conducting thorough literature reviews. Sifting through countless articles, organizing references, and identifying key themes can feel overwhelming. But what if there was a tool that could streamline this process and make it more efficient? Enter Litmaps, your new secret weapon for conquering literature reviews:)
What is Litmaps?
Litmaps is a powerful online platform that helps researchers, students, and professionals navigate the vast world of scientific literature. It uses advanced algorithms to analyze your chosen seed articles and generate a comprehensive map of related research, highlighting key themes, authors, and citations.
Why should your students use Litmaps?
- Save time and effort: Litmaps automates the tedious process of finding relevant articles, saving you hours of searching and filtering.
- Gain a deeper understanding: Visualize the connections between different research areas and identify key trends and gaps in the literature.
- Improve research quality: Ensure your literature review is comprehensive and well-supported by relevant sources.
- Boost collaboration: Share your Litmaps with colleagues or classmates to discuss findings and refine your research strategy.
- Stay up-to-date: Receive automatic updates on new publications related to your topic, keeping you at the forefront of your field.
More than just a tool, Litmaps is a learning experience.
By introducing Litmaps to your students, you equip them with a powerful tool that will enhance their research skills, improve the quality of their work, and ultimately, contribute to their academic success. So, unlock the potential of Litmaps and watch your students transform their approach to literature reviews.
1.Navigate to https://www.litmaps.com/
2.Search by keyword: (for example: systemic racism)
3.Choose some starting articles to kickstart your Litmap.
4.Create Litmap.

Kevin Scott on AI and Humanism (YouTube)
🔧 Scott’s passion for cooking and woodworking stems from his upbringing in a family that valued DIY projects. This background influenced his career as an engineer, where he builds and creates with code, complementing his hands-on hobbies.
💼 The partnership between Microsoft and OpenAI was a crucial decision driven by the recognition that AI advancements were accelerating rapidly. Scott saw the need for Microsoft to develop a competitive AI platform, which required building powerful infrastructure and allocating resources effectively.
🌍 Partnerships are integral to building and scaling transformative platforms. Scott emphasizes the importance of collaboration and the recognition that no single entity can create a world-changing platform alone. Partnerships enable progress by combining expertise and resources.
💡 AI has the potential to benefit society in various domains, such as healthcare and job productivity. Scott believes that AI can augment human capabilities and provide solutions to complex problems, leading to improved quality of life and increased productivity.
🔄 The coexistence of humans and AI will involve humans leveraging AI to amplify their abilities. The goal is not to replace humans but to enhance their potential. Scott believes that humans will continue to play a vital role in decision-making and creativity, while AI assists and supports them.
📈 The progress of AI has exceeded many expectations, with advancements happening faster than predicted. Scott acknowledges the skepticism surrounding AI and emphasizes the importance of continuous improvement, feedback loops, and collaboration to ensure responsible and beneficial AI development.
🌱 AI, combined with technological tools, has the potential to revitalize communities and empower individuals. The accessibility and power of these tools can create opportunities for economic growth and innovation, even in rural areas, by leveraging technology and expertise.